4-1-Shell快速入门
SHELL编程导学
该课程主要包括以下内容:
① Shell的基本语法结构
如:变量定义、条件判断、循环语句(for、until、while)、分支语句、函数和数组等;
② 基本正则表达式的运用;
③ 文件处理三剑客:grep、sed、awk工具的使用;
④ 使用shell脚本完成一些较复杂的任务,如:服务搭建、批量处理等。
说明:以上内容仅仅是基本要求,还有很多更深更难的语法需要扩充学习。
今日目标
- 熟悉grep、cut、sort等小工具和shell中的通配符的使用
- ==熟练掌握shell变量的定义和获取(重点)==
- ==能够进行shell简单的四则运算==
- ==熟悉条件判断语句,如判断整数,判断字符串等==
1.编程语言
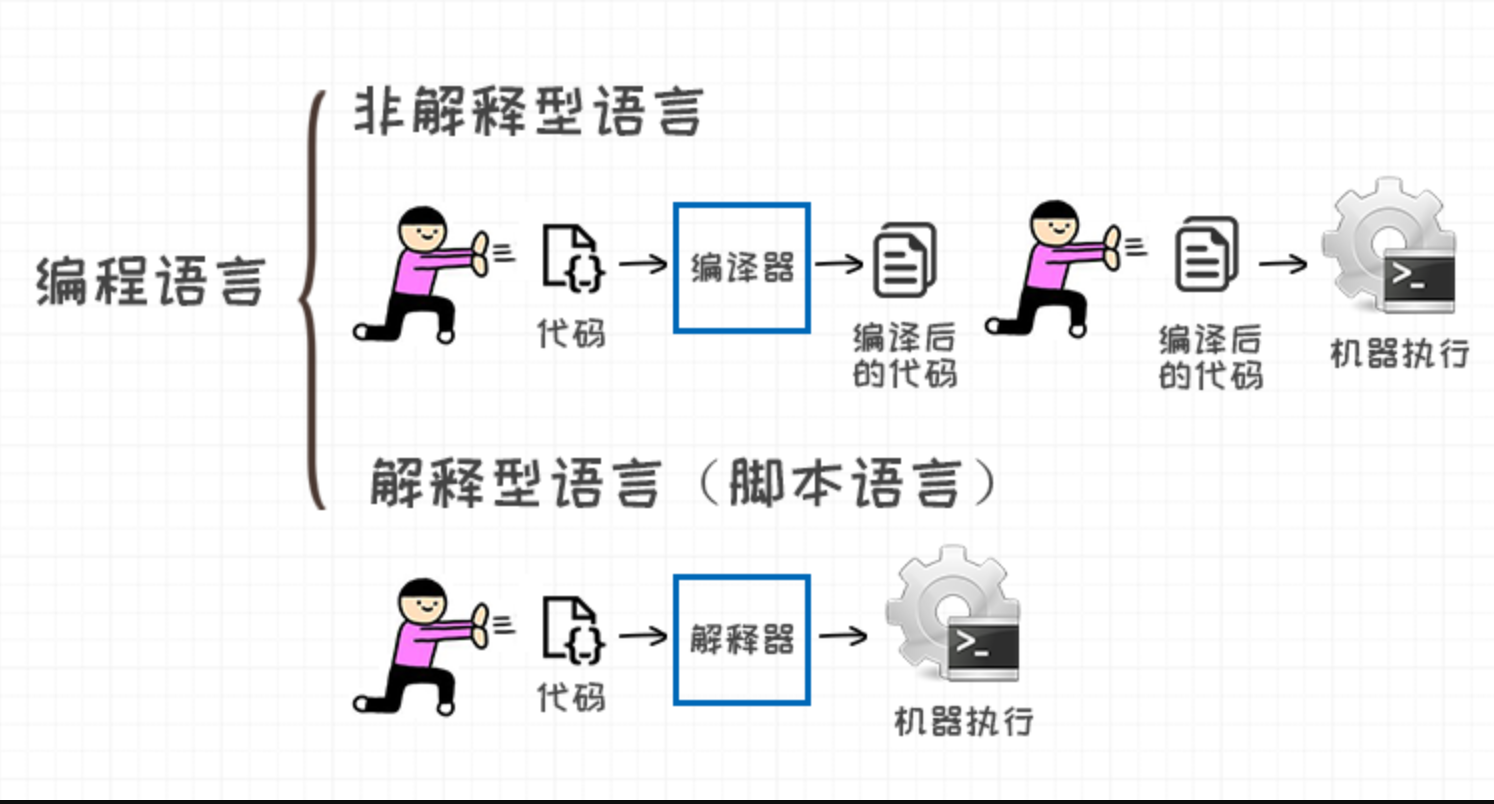
1.1 编译型语言
程序在执行之前需要一个专门的编译过程,把程序编译成为机器语言文件,运行时不需要重新翻译,直接使用编译的结果就行了。
程序执行效率高,依赖编译器,跨平台性差些。如C、C++。
演示go语言,进行代码编译,运行
1.安装golang编译器
[root@yuchao-linux01 ~]# yum install golang -y
2.编写golang代码
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# cat hello.go
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("于超老师带你学Linux")
}
3.编译代码,生成二进制命令
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# go mod init hello_yc
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# ./hello_yc
于超老师带你学Linux
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# file hello_yc
hello_yc: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, not stripped
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]#
4.加入到PATH变量中
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# mv hello_yc /usr/local/sbin/
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]#
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# hello_yc
于超老师带你学Linux
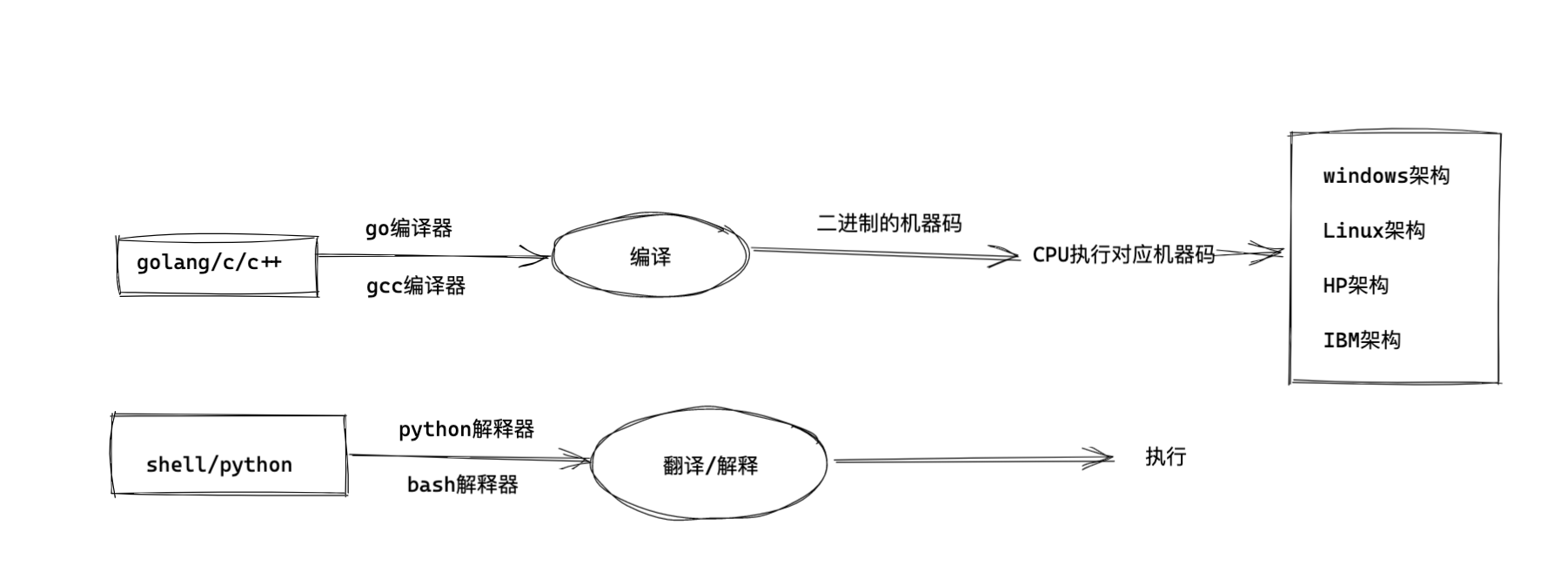
1.2 解释型语言
程序不需要编译,程序在运行时由==解释器==翻译成机器语言,每执行一次都要翻译一次。
因此效率比较低。比如Python/JavaScript/ Perl /ruby/Shell等都是解释型语言。
python脚本
1.安装python3
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# yum install python3 python3-devel -y
2.写代码
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# cat hello.py
print("于超老师带你学linux")
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]#
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# python3 hello.py
于超老师带你学linux
bash脚本
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# cat hello.sh
echo "于超老师带你学linux"
[root@yuchao-tx-server about_shell]# bash hello.sh
于超老师带你学linux
1.3 区别
编译型语言比解释型语言==速度较快==,但是不如解释型语言==跨平台性好==。
如果做底层开发或者大型应用程序或者操作系开发一==般都用编译型语言==;
如果是一些服务器脚本及一些辅助的接口,对速度要求不高、对各个平台的==兼容性有要求==的话则一般都用==解释型语言==。
2. shell介绍
- ==shell就是运维、linux交互的一个桥梁==
- shell的种类
/bin/sh #是bash shell的一个快捷方式
/bin/bash #bash shell是大多数Linux默认的shell,包含的功能几乎可以涵盖shell所有的功能
/sbin/nologin #表示非交互,不能登录操作系统
/bin/dash #小巧,高效,功能相比少一些
/bin/tcsh #是csh的增强版,完全兼容csh
/bin/csh #具有C语言风格的一种shell,具有许多特性,但也有一些缺陷
还有一些现在很火的zsh,个人美化终端shell
- 用户在终端输入命令(终端就是bash的输入口)
用户 > bash > kernel > 机器硬件(cpu)
2.1 shell脚本
什么是shell脚本?
- 一句话概括
简单来说就是将需要执行的命令保存到文本中,==按照顺序执行==。它是解释型的,意味着不需要编译。
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# cat hello.sh
echo '我是超哥1'
echo '我是超哥2'
echo '我是超哥3'
echo '我是超哥4'
echo '我是超哥5'
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# bash hello.sh
我是超哥1
我是超哥2
我是超哥3
我是超哥4
我是超哥5
- 准确叙述
若干命令 + 脚本的基本格式 + 脚本特定语法 + 思想= shell脚本
[root@web01 ~]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
# testing the if statement
if pwd
then
echo "It worked"
fi
[root@web01 ~]#
[root@web01 ~]# bash test.sh
/root
It worked
什么时候用到脚本?
重复化、复杂化的工作,通过把工作的命令写成脚本,以后仅仅需要执行脚本就能完成这些工作。
①自动化分析处理
②自动化备份
③自动化批量部署安装
④等等...
如何学习shell脚本?
- 尽可能记忆更多的命令;
- 掌握脚本的标准的格式、使用标准的执行方式运行脚本;
- 必须==熟悉掌握==脚本的基本语法(重点)
学习脚本的秘诀
多看(看懂)——>多模仿(多练)——>多思考
脚本基本写法
#!/bin/bash
脚本第一行, #!魔法字符(shebang),指定脚本代码执行的程序。
即它告诉系统这个脚本需要什么解释器来执行,也就是使用哪一种Shell
以下内容是对脚本的基本信息的描述
# Name: 名字
# Desc:描述describe
# Path:存放路径
# Usage:用法
# Update:更新时间
下面就是脚本的具体内容
commands
...
脚本执行方法
- 标准写法
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# cat hello.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo '我是超哥1'
echo '我是超哥2'
echo '我是超哥3'
echo '我是超哥4'
echo '我是超哥5'
echo '当前时间' $(date "+%F %T")
echo '当前主机名' $(hostname)
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# ./hello.sh
我是超哥1
我是超哥2
我是超哥3
我是超哥4
我是超哥5
当前时间 2021-12-12 09:38:05
当前主机名 yuchao-linux01
- 非标准写法(指定解释器运行脚本,会覆盖shebang)
当脚本没有x执行权限的时候,我们可以采用bash直接解释运行。
语法参数
bash file.sh
-x: 一般用于排错,查看脚本的执行过程
-n: 用来查看脚本的语法是否有问题
bash解释器直接运行脚本
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# bash hello.sh
我是超哥1
我是超哥2
我是超哥3
我是超哥4
我是超哥5
当前时间 2021-12-12 09:39:05
当前主机名 yuchao-linux01
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# sh hello.sh
我是超哥1
我是超哥2
我是超哥3
我是超哥4
我是超哥5
当前时间 2021-12-12 09:39:13
当前主机名 yuchao-linux01
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# bash -x hello.sh
+ echo 我是超哥1
我是超哥1
+ echo 我是超哥2
我是超哥2
+ echo 我是超哥3
我是超哥3
+ echo 我是超哥4
我是超哥4
+ echo 我是超哥5
我是超哥5
++ date '+%F %T'
+ echo 当前时间 2021-12-12 09:39:23
当前时间 2021-12-12 09:39:23
++ hostname
+ echo 当前主机名 yuchao-linux01
当前主机名 yuchao-linux01
使用source命令或.运行
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# source hello.sh
我是超哥1
我是超哥2
我是超哥3
我是超哥4
我是超哥5
当前时间 2021-12-12 09:44:31
当前主机名 yuchao-linux01
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]#
[root@yuchao-linux01 shell_dir]# . hello.sh
我是超哥1
我是超哥2
我是超哥3
我是超哥4
我是超哥5
当前时间 2021-12-12 09:44:33
当前主机名 yuchao-linux01
执行方式总结
- 添加shebang,x执行权限,./file.sh运行
bash/sh运行
Source/. 运行
具体区别,是否开辟子shell去运行程序。